Architecture
Obot is designed to enable organizations to consume MCP servers in an enterprise setting. It consists of four core components: MCP Hosting for running servers, MCP Registry for discovery, MCP Gateway for access control, and Obot Chat for user interaction.
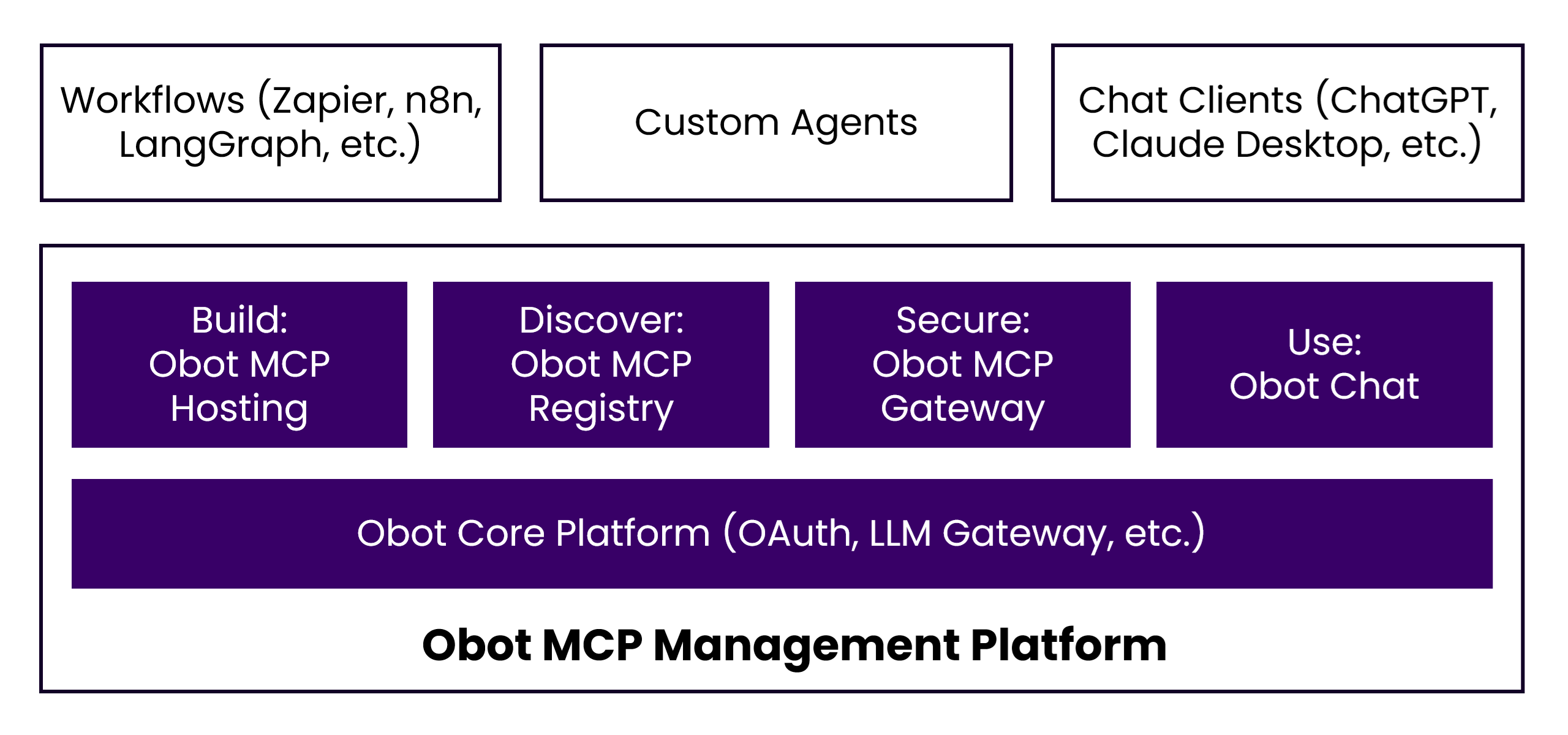
Key Concepts
-
MCP Clients: Tools that interact with LLMs and consume MCP servers. These include agents, desktop tools like Cursor, Claude Desktop, VS Code, and Obot Chat.
-
MCP Servers: Code that implements the MCP specification (tools, prompts, resources) for consumption by clients.
-
MCP Registry: An index of MCP servers with metadata about how to run them and where to find them.
-
MCP Gateway: A reverse-proxy that authenticates users, ensures servers are deployed, and forwards requests. See MCP Gateway for details.
-
MCP Server Shim: A protocol-aware sidecar that runs alongside each MCP server, handling authorization, audit logging, webhook filters, and token exchange.
-
MCP Hosting: Infrastructure for running MCP server containers (Docker or Kubernetes).
-
LLM Gateway: A proxy between chat clients and LLMs that enables monitoring and control of LLM communications.
Authentication Flow
All clients first authenticate with Obot via the configured identity provider. The gateway validates the user and proxies the request to the MCP Server Shim. The shim then handles authorization checks and, if the MCP server requires it, performs OAuth token exchange (RFC 8693) to obtain a third-party access token.
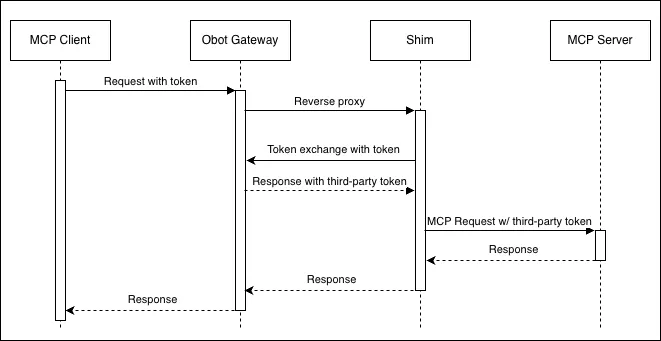
Key security properties:
- Gateway: Handles user authentication only
- MCP Server Shim: Handles authorization, audit logging, and token exchange
- Secret isolation: Credentials for token exchange live in the MCP Server Shim, never exposed to the MCP server. MCP server configuration is never exposed to the MCP Server Shim.
Data Persistence
- Database: Postgres for storing configuration and metadata. In production, this should be hosted independently of the Obot deployment.
- Object Storage: S3-compatible storage for workspace data (PDFs, text files, etc.)
Encryption
Obot uses cloud KMS systems to encrypt data at rest. See Encryption Providers for configuration options.
LLMs
Obot operates with a bring-your-own-model philosophy. Multiple providers can be configured to meet organizational requirements. See Model Providers for details.